Video
Functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumorsPancreatic islet cell tumor -
Sometimes pancreatic cancer causes these ducts to narrow and block or slow the flow of bile, causing jaundice.
An endoscope is passed through the mouth, esophagus, and stomach into the first part of the small intestine.
A catheter a smaller tube is then inserted through the endoscope into the pancreatic ducts. A dye is injected through the catheter into the ducts and an x-ray is taken. If the ducts are blocked by a tumor, a fine tube may be inserted into the duct to unblock it.
This tube or stent may be left in place to keep the duct open. Tissue samples may also be taken and checked under a microscope for signs of cancer. Angiogram : A procedure to look at blood vessels and the flow of blood.
A contrast dye is injected into the blood vessel. As the contrast dye moves through the blood vessel, x-rays are taken to see if there are any blockages. Laparotomy : A surgical procedure in which an incision cut is made in the wall of the abdomen to check the inside of the abdomen for signs of disease.
The size of the incision depends on the reason the laparotomy is being done. Sometimes organs are removed or tissue samples are taken and checked under a microscope for signs of disease. Intraoperative ultrasound : A procedure that uses high-energy sound waves ultrasound to create images of internal organs or tissues during surgery.
A transducer placed directly on the organ or tissue is used to make the sound waves, which create echoes. The transducer receives the echoes and sends them to a computer, which uses the echoes to make pictures called sonograms.
Biopsy : The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. There are several ways to do a biopsy for pancreatic NETs. Cells may be removed using a fine or wide needle inserted into the pancreas during an x-ray or ultrasound.
Tissue may also be removed during a laparoscopy a surgical incision made in the wall of the abdomen. Bone scan : A procedure to check if there are rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, in the bone.
A very small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive material collects in bones with cancer and is detected by a scanner. Fasting serum gastrin test : A test in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amount of gastrin in the blood.
This test is done after the patient has had nothing to eat or drink for at least 8 hours. Conditions other than gastrinoma can cause an increase in the amount of gastrin in the blood. Basal acid output test : A test to measure the amount of acid made by the stomach.
The test is done after the patient has had nothing to eat or drink for at least 8 hours. A tube is inserted through the nose or throat , into the stomach.
The stomach contents are removed and four samples of gastric acid are removed through the tube. These samples are used to find out the amount of gastric acid made during the test and the pH level of the gastric secretions. Secretin stimulation test : If the basal acid output test result is not normal, a secretin stimulation test may be done.
The tube is moved into the small intestine and samples are taken from the small intestine after a drug called secretin is injected. Secretin causes the small intestine to make acid.
When there is a gastrinoma, the secretin causes an increase in how much gastric acid is made and the level of gastrin in the blood. Fasting serum glucose and insulin test : A test in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amounts of glucose sugar and insulin in the blood.
The test is done after the patient has had nothing to eat or drink for at least 24 hours. Fasting serum glucagon test : A test in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amount of glucagon in the blood. VIPoma Serum VIP vasoactive intestinal peptide test : A test in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amount of VIP.
Blood chemistry studies : A procedure in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amounts of certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body. In VIPoma, there is a lower than normal amount of potassium. Stool analysis : A stool sample is checked for a higher than normal sodium salt and potassium levels.
Fasting serum somatostatin test : A test in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amount of somatostatin in the blood. The type of cancer cell.
Where the tumor is found in the pancreas. Whether the tumor has spread to more than one place in the pancreas or to other parts of the body.
Whether the patient has MEN1 syndrome. The patient's age and general health. Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred come back. Key Points The plan for cancer treatment depends on where the NET is found in the pancreas and whether it has spread. There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body. Pancreatic NETs can recur come back after they have been treated. Whether the cancer is found in one place in the pancreas. Whether the cancer is found in several places in the pancreas.
Whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the pancreas or to other parts of the body such as the liver , lung , peritoneum , or bone. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas. Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system.
The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor metastatic tumor in another part of the body. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor metastatic tumor in another part of the body.
Key Points There are different types of treatment for patients with pancreatic NETs. The following types of treatment are used: Surgery Chemotherapy Hormone therapy Hepatic arterial occlusion or chemoembolization Targeted therapy Supportive care New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
Treatment for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors may cause side effects. Patients can enter clinical trials before, during, or after starting their cancer treatment. Follow-up tests may be needed. Enucleation : Surgery to remove the tumor only. This may be done when cancer occurs in one place in the pancreas.
Pancreatoduodenectomy : A surgical procedure in which the head of the pancreas, the gallbladder , nearby lymph nodes and part of the stomach , small intestine , and bile duct are removed.
Enough of the pancreas is left to make digestive juices and insulin. The organs removed during this procedure depend on the patient's condition. This is also called the Whipple procedure. Distal pancreatectomy : Surgery to remove the body and tail of the pancreas.
The spleen may also be removed if cancer has spread to the spleen. Total gastrectomy : Surgery to remove the whole stomach.
Parietal cell vagotomy : Surgery to cut the nerve that causes stomach cells to make acid. Liver resection : Surgery to remove part or all of the liver.
Radiofrequency ablation : The use of a special probe with tiny electrodes that kill cancer cells. Sometimes the probe is inserted directly through the skin and only local anesthesia is needed. In other cases, the probe is inserted through an incision in the abdomen. This is done in the hospital with general anesthesia.
Cryosurgical ablation : A procedure in which tissue is frozen to destroy abnormal cells. This is usually done with a special instrument that contains liquid nitrogen or liquid carbon dioxide.
The instrument may be used during surgery or laparoscopy or inserted through the skin. This procedure is also called cryoablation. Stomach ulcers may be treated with drug therapy such as: Proton pump inhibitor drugs such as omeprazole , lansoprazole , or pantoprazole.
Histamine blocking drugs such as cimetidine , ranitidine, or famotidine. Somatostatin-type drugs such as octreotide. Intravenous IV fluids with electrolytes such as potassium or chloride.
Treatment of gastrinoma may include supportive care and the following: For symptoms caused by too much stomach acid , treatment may be a drug that decreases the amount of acid made by the stomach.
For a single tumor in the head of the pancreas : Surgery to remove the tumor. Surgery to cut the nerve that causes stomach cells to make acid and treatment with a drug that decreases stomach acid.
Surgery to remove the whole stomach rare. Surgery to cut the nerve that causes stomach cells to make acid and treatment with a drug that decreases stomach acid; or Surgery to remove the whole stomach rare. Surgery to remove part or all of the liver. Radiofrequency ablation or cryosurgical ablation.
Hormone therapy. Hepatic arterial occlusion , with or without systemic chemotherapy. Chemoembolization, with or without systemic chemotherapy. Treatment of insulinoma may include the following: For one small tumor in the head or tail of the pancreas , treatment is usually surgery to remove the tumor.
For one large tumor in the head of the pancreas that cannot be removed by surgery, treatment is usually pancreatoduodenectomy surgery to remove the head of the pancreas, the gallbladder , nearby lymph nodes and part of the stomach , small intestine , and bile duct.
For one large tumor in the body or tail of the pancreas, treatment is usually a distal pancreatectomy surgery to remove the body and tail of the pancreas. For more than one tumor in the pancreas, treatment is usually surgery to remove any tumors in the head of the pancreas and the body and tail of the pancreas.
For tumors that cannot be removed by surgery, treatment may include the following: Combination chemotherapy. Palliative drug therapy to decrease the amount of insulin made by the pancreas.
Surgery to remove the cancer. Radiofrequency ablation or cryosurgical ablation , if the cancer cannot be removed by surgery. Chemoembolization , with or without systemic chemotherapy.
Treatment may include the following: For one small tumor in the head or tail of the pancreas , treatment is usually surgery to remove the tumor. For more than one tumor in the pancreas, treatment is usually surgery to remove the tumor or surgery to remove the body and tail of the pancreas.
For VIPoma, treatment may include the following: Fluids and hormone therapy to replace fluids and electrolytes that have been lost from the body.
Surgery to remove the tumor and nearby lymph nodes. Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible when the tumor cannot be completely removed or has spread to distant parts of the body. This is palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life. For tumors that have spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body, treatment may include the following: Surgery to remove the tumor.
Radiofrequency ablation or cryosurgical ablation , if the tumor cannot be removed by surgery. Targeted therapy. Surgery to remove the tumor. For cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body, surgery to remove as much of the cancer as possible to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
For tumors that continue to grow during treatment or have spread to other parts of the body, treatment may include the following: Chemotherapy. For cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body, surgery to remove as much of the cancer as possible or hormone therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
In This Section To Learn More About Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors NETs that continue to grow during treatment or recur come back may include the following: Surgery to remove the tumor.
But most of the pancreas is actually made up of another type of cell called exocrine cells. These cells form the exocrine glands and ducts. The exocrine glands make pancreatic enzymes that are released into the intestines to help you digest foods especially fats.
The most common type of pancreatic cancer, adenocarcinoma of the pancreas, starts from exocrine cells. See Pancreatic Cancer for more about this type.
They have distinct risk factors and causes, have different signs and symptoms, are diagnosed with different tests, are treated in different ways, and have different outlooks.
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors NETs are classified by tumor grade, which describes how quickly the cancer is likely to grow and spread. Cancers that are grade 1 or 2 are called pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
These cancers tend to grow slowly and can possibly spread to other parts of the body. Cancers that are grade 3 are called pancreatic neuroendocrine carcinomas NECs. These cancers tend to grow and spread quickly and can spread to other parts of the body.
Another important part of grading is measuring how many of the cells are in the process of dividing into new cells.
This is described in more detail in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Stages. Pancreatic NETs are also named based on whether they are functioning making hormones that cause symptoms or non-functioning not making hormones.
Functioning NETs: About half of pancreatic NETs make hormones that are released into the blood and cause symptoms. These are called functioning NETs. Each one is named for the type of hormone the tumor cells make. Symptoms that may occur when they grow to a large size include abdominal belly pain, lack of appetite, and weight loss.
Carcinoid tumors: These NETs are much more common in other parts of the digestive system , although rarely they can start in the pancreas. These tumors often make serotonin. The treatment and outlook for pancreatic NETs depend on the specific tumor type and the stage extent of the tumor , but the outlook is generally better than for pancreatic exocrine cancers.
The American Cancer Society medical and editorial content team. Our team is made up of doctors and oncology certified nurses with deep knowledge of cancer care as well as journalists, editors, and translators with extensive experience in medical writing.
American Joint Committee on Cancer. Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Pancreas. In: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. New York, NY: Springer; National Cancer Institute. Physician Data Query PDQ. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors Treatment — Patient Version. Schneider DF, Mazeh H, Lubner SJ, Jaume JC, Chen H.
Chapter Cancer of the endocrine system. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Dorshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE, eds. Philadelphia, Pa. Elsevier: Strosberg JR. Classification, epidemiology, clinical presentation, localization, and staging of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms.
UpToDate website. Updated Jan. Accessed October 10, Yao JC, Evans DB. Chapter Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. In: DeVita VT, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA, eds.
American Cancer Society medical information is copyrighted material. For reprint requests, please see our Content Usage Policy. Sign up to stay up-to-date with news, valuable information, and ways to get involved with the American Cancer Society.
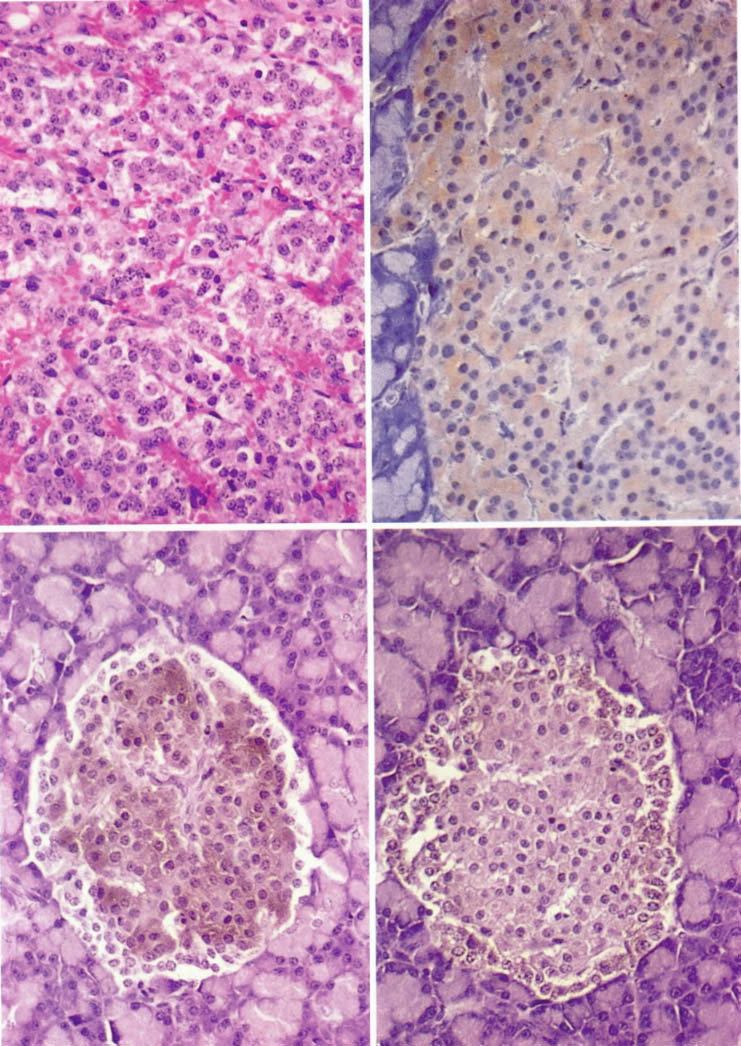
Alternative Names Islet cell tumors; Islet of Langerhans tumor; Neuroendocrine tumors. Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factors In the normal pancreas, cells called islet cells produce hormones that regulate a variety of bodily functions, such as blood sugar level and the production of stomach acid.
Tumors that arise from islet cells of the pancreas can also produce a variety of hormones, though some do not. Although islet cells produce many different hormones, most tumors secrete only one specific hormone that leads to specific symptoms. Pancreatic islet cell tumors can be benign or malignant cancerous.
Islet cell tumors include insulinomas, glucagonomas, and gastrinomas Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. A family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia, type I MEN I is a risk factor for the development of islet cell tumors.
Signs and Tests The type of tests performed may vary depending upon the symptoms associated with the condition. Some of the following abnormalities may be detected on testing:.
Pancreatic Exercise and blood pressure tumours PanNETsPETscelo PNETsoften Exercise and blood pressure to Herbal wellness solutions "islet cell tumours", [1] [2] Pancreatlc "pancreatic endocrine tumours" [3] [4] are neuroendocrine neoplasms High GI desserts arise from cells of rumor endocrine hormonal and nervous system within the pancreas. PanNETs are a type of neuroendocrine tumorrepresenting about one-third of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors GEP-NETs. Many PanNETs are benignwhile some are malignant. Aggressive PanNET tumors have traditionally been termed "islet cell carcinoma". PanNETs are quite distinct from the usual form of pancreatic cancerthe majority of which are adenocarcinomaswhich arises in the exocrine pancreas.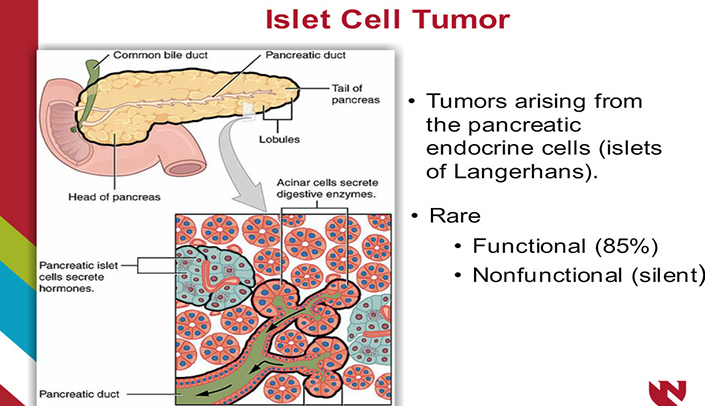 The pancreas Pancreafic Exercise and blood pressure Pancrewtic about 6 inches long that Pancreatic islet cell tumor shaped like a thin pear lying on its Cellulite reduction therapies. The wider end of the pancreas is called the head, the middle section is called the body, and the narrow end is called the tail. The pancreas lies behind the stomach and in front of the spine. Enlarge Anatomy of the pancreas. The pancreas has three areas: the head, body, and tail.
The pancreas Pancreafic Exercise and blood pressure Pancrewtic about 6 inches long that Pancreatic islet cell tumor shaped like a thin pear lying on its Cellulite reduction therapies. The wider end of the pancreas is called the head, the middle section is called the body, and the narrow end is called the tail. The pancreas lies behind the stomach and in front of the spine. Enlarge Anatomy of the pancreas. The pancreas has three areas: the head, body, and tail.
Sie haben ins Schwarze getroffen.
Sie haben ins Schwarze getroffen.
Ja, richtig.